In this article, we will share basic information about synthetic assets in simple language. If you want to be fluent in the intricacies of decentralized finance, you cannot pass by this class of blockchain-based financial tools!
What Are Synthetics?
Tokenized derivatives from various assets are called synthetics. A derivative in classical finance is a financial contract whose value depends on stocks or bonds that the investor does not actually own but is using in order to exploit their price movements. Derivatives were invented to make money on fluctuations in the prices of assets without having to buy them.
Synthetic assets are a step forward in this direction. In contrast to classic derivatives (which are recorded on paper or in an electronic ledger), synthetic assets record data about derivatives in the blockchain, issuing the corresponding crypto-tokens.
Synthetic assets may consist of one or more derivatives based on the values of underlying assets. These include:
- Forward commitments – a contractual agreement to carry out a specified transaction in the future. Examples are futures, forwards, and swaps;
- Contingent claims – a derivative whose future payoff depends on the value of another “underlying” asset or the realization of some uncertain future event. Examples are options, credit derivatives such as credit default swaps (CDS), and asset-backed securities.
Synthetic assets record the relationship between the underlying asset and the purchaser on the blockchain. It is a very handy tool that allows investors and traders to take advantage of the price changes of any asset without having to store them in their wallets. They bring traditional financial instruments to the DeFi sector, increasing its versatility.
How It works
In the crypto space reality, the use of synthetics can be described as: “This is how you speculate on the price of BTC without buying any BTC.”
For a better understanding of how synthetic assets are obtained, we give the example of the creation of synthetic Bitcoin (fictional uBTC) on the Tezos blockchain:
- The issuer sets up oracles to get Bitcoin prices from several exchanges.
- They then create a vault and a uBTC token and determine the collateral factor applicable to the synthetic Bitcoin.
- Users deposit Tez in the vault and issue the synthetic uBTC.
- The vault’s smart contract continuously receives new Bitcoin prices from the selected exchanges and revises the price of new uBTC.
- As a result, the Tezos blockchain now has a token that is worth 1 BTC and is collateralized by Tez.
By creating a synthetic asset, you can refer the cost of several underlying assets to it at once, which is convenient and safer in terms of hedging risks.
What Are Synthetics Good For?
As we mentioned above, synthetic assets allow you to tokenize and trade any asset. The advantage of synthetic assets over classical market derivatives is their reliability and versatility: you can create a derivative instrument, issue its token, and use it within the blockchain at your own discretion. In addition, synthetic assets allow you to maintain anonymity as the “owner” of tokenized shares of some large company, which is simply impossible in traditional finance.
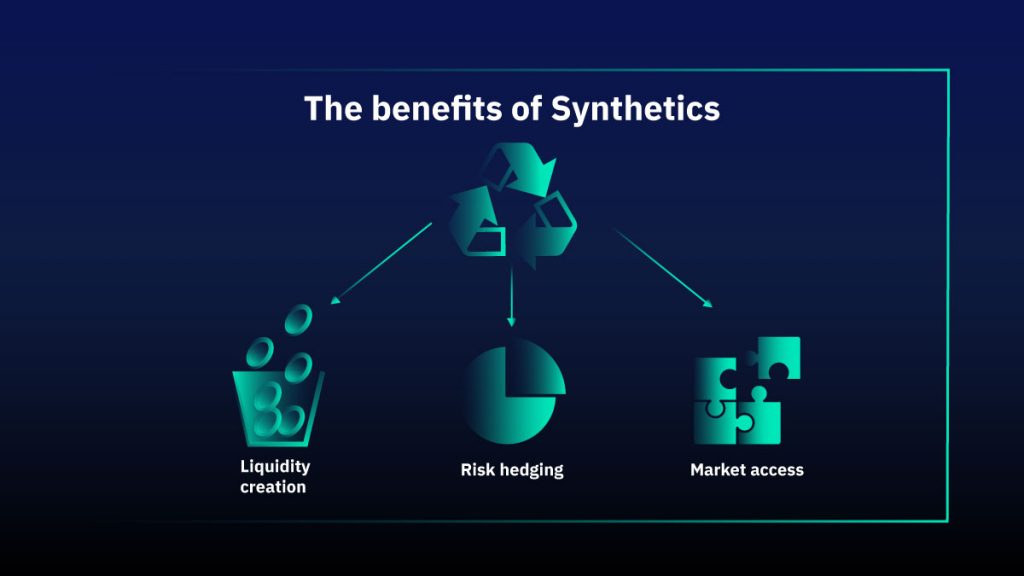
The advantages of synthetic assets in the blockchain ecosystem relative to the traditional market are as follows:
Liquidity creation
Synthetic assets inject liquidity into the market. One example is a credit default swap. A CDS is a derivative contract between a buyer and seller, offering the buyer credit protection. The buyer makes payments to the seller in exchange for a promise of repayment of losses associated with a “credit event” such as a failure to pay, bankruptcy, or restructuring. The seller takes a synthetic long position in the underlying asset, and the buyer hedges the risks.
Risk hedging
A synthetic asset allows you to add the value of several underlying assets to its “composition” at once, which will be tracked by the oracles. Thus, a trader can insure himself against a fall in the value of several assets, subject to the growth of the rest.
Market access
Synthetic products can open the market to relatively free participation by recreating the cash flows of virtually any security through the use of a combination of instruments and derivatives. This allows you to benefit from changes in the prices of assets that are difficult to obtain in the traditional market. For those who cannot purchase bonds, stocks, or other instruments that require a high degree of compliance with audits and regulators, it is easier to own a synthetic asset that reflects their value.
Synthetics & DeFi
Without the blockchain, synthetic assets are just “paper bets” that are enforced by legal contracts. Before the advent of decentralized finance, synthetic assets were only available to banks and large investment companies. After smart contracts came into play, the creation and use of a tokenized derivative became available to a wider audience.
There are several reasons why synthetics can be useful to multiple participants in the DeFi ecosystem:
- Scaling assets: Synthetic assets are an alternative approach to issuing secured stablecoins. They remove the need for you to keep the actual asset in custody with a centralized counterparty.
- Scaling liquidity: More broadly, synthetics and derivatives can help decentralized financial markets expand by hedging positions and protecting profits.
- Scaling technology: The problem of cross-chain communication of assets is still present in decentralized protocols. The creation of synthetic assets will allow you to use the price fluctuations of any asset in any blockchain.
- Scaling participation: Synthetic assets provide a wider range of users with access to tokenized derivatives. This can attract more players who want to hedge their risks to the market.
Synthetics vs. Wrapped Assets
Although synthetics allow you to tokenize any asset by moving it to the blockchain, they are different from wrapped assets. Wrapped assets require a specific asset to be locked in the original environment (on the blockchain) in order to issue the wrapped tokens on the selected blockchain at a 1:1 ratio.
In fact, synthetic assets do not require the blocking of the original asset. They only need an oracle that will track the price and provide it to the smart contract. Synthetic assets are also used as bets on the changes in the price of an asset. They represent your share of the bet against other players (derivatives).
More details on Wrap protocols and their mechanisms are available at this link
Risks
First of all, synthetic assets can be used to predict changes in asset prices and make money on them. Any form of trading is associated with additional risks and financial losses.
Moreover, oracles that provide information on the prices of certain assets as part of a synthetic token represent the participation of an intermediary, which can lead to additional problems. Oracles can knowingly or unknowingly make a mistake in the information provided, and this may lead to a derivative instrument such as a synthetic asset losing its relation to the value of the real assets.
You can find out more about oracles, their advantages, and disadvantages in our full review.
In addition, blockchain protocols or platforms can be hacked through code vulnerabilities. Such interference by fraudsters can lead to the loss of funds and other unpleasant consequences. (How to protect your funds in crypto from scammers — instructions)
The Most Popular Synthetic Platforms in DeFi
The decentralized finance market offers a wide variety of instruments for working with synthetic assets. The most popular tokenized derivatives exchange at the moment is Synthetix. The TVL in Synthetix protocols exceeds $1 billion. The platform allows the creation of synthetic assets that can be used across a range of ecosystem products in the DeFi industry.
Cream Finance and MakerDAO are two popular alternatives to Synthetix.
Cream Finance is a multi-chain landing protocol that focuses on longtail assets. Users can lend out any supported assets and use the provided capital as collateral to borrow others You can also create synthetic assets with Cream Finance.
MakerDAO implements decentralized loans on Ethereum to create the Dai stablecoin. Dai is essentially a synthetic US dollar, which can also be used to create other synthetic assets (both cryptocurrency and fiat).
Synthetics on Tezos
Synthetic assets are also used on the Tezos blockchain since it currently offers a convenient basis for decentralized finance with a growing ecosystem.
Youves is a platform for issuing synthetic assets on the Tezos blockchain. You can use the TEZ token as collateral and issue any other synthetic asset on its basis.
SEXP (Synthetic Exchange Project) is a DEX for trading synthetic assets built on Tezos. The platform uses the Harbinger oracles and the Kolibri kUSD token to secure open derivative positions. The full launch of the platform is planned for 2022.
Conclusions
Synthetic assets significantly improve decentralized finance by providing crypto enthusiasts with convenient tools for classic trading and considerably expanding the user base of derivatives. DeFi allows access to synthetic assets even for those categories of users for whom it would otherwise be unavailable in the traditional financial system. In addition, since transactions for the creation and sale of synthetic assets are implemented through smart contracts and blockchain, this provides both additional security and new liquidity to the crypto market.