Privacy or anonymous blockchains and cryptocurrencies are separate directions of decentralized technologies. Their main goal is to make it impossible to track transaction details, including sender and recipient addresses. Instead, they allow users to hide their traces in a blockchain, actively using it.
In this article, we’ll define “privacy coins”, explain why most famous cryptocurrencies aren’t as anonymous as they want to be, and describe how privacy coins ensure privacy in practice.
Are Popular Cryptocurrencies Not Anonymous?
It is common to come across words such as “anonymous” or “confidential” when cryptocurrencies are being described. In some sense, these descriptions are true because it is not required to provide any personal data to third parties before sending, receiving, or holding crypto. For those who want to start dealing with crypto, it is usually enough to create a crypto address and save its private key or seed phrase. But keeping in mind such things as “public”, or “transparent,” describing crypto, newcomers may have a conflict of understanding.
The thing is that although users don’t disclose their personal data, the entire transactions’ history and each wallet’s activity are invariably stored in a decentralized data registry which is available to everyone using a blockchain explorer. So once someone successfully discovers the identity behind an address, all the benefits of so-called anonymity will be abolished.
For example, companies such as Chainalysis are creating tools to deanonymize transactions on the blockchain. For instance, it may be useful for law enforcement agencies to search for criminals’ identities. Often, this deanonymization process is successful, and the identity behind a particular address is uncovered.
Looking For Privacy
Since confidentiality is one of the most critical advantages of cryptocurrencies, the community has strived to solve this problem in any possible way. In Bitcoin’s case, we can point to the Taproot Upgrade. In addition to accelerating network processing by batching multiple signatures and transactions together, it also scrambles transactions with single and multiple signatures together. It thus makes it more challenging to identify transaction inputs on Bitcoin’s blockchain. You can learn more about Bitcoin’s Taproot update here.
Additionally, another one of the most popular tools for “obfuscating” coins on the network and “cleansing” their transaction history is a crypto mixer. Such a service accepts BTC from several users and then mixes and distributes them among participants in the same proportions (minus the fees).
Using mixers leads to a situation in which a particular address contains the same amount of BTC as it had before mixing, but different UTXO data (detailed info about the UTXO model and how the bitcoin ledger works can be found here). The mixer makes it much more difficult to track the coin’s history on the network. Among popular mixers are Blender.io, CoinJoin, and CoinSwap.
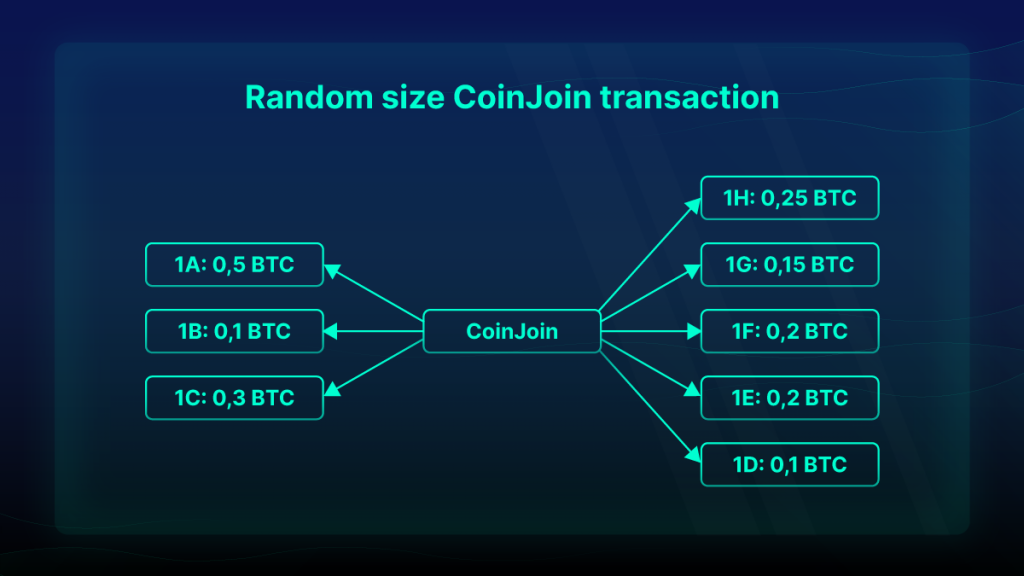
But there is also a third way to achieve high privacy, namely, privacy networks.
What Is a Privacy Blockchain?
The answer to this question is pretty simple. A privacy blockchain is a decentralized distributed ledger, like Bitcoin or Ethereum, but which places emphasis on the anonymity and opacity of events inside the network. However, they are usually kept running by independent validators (nodes) that confirm transactions according to predefined rules. The most significant privacy coins by market capitalization are Zcash and Monero, but several years ago, Dash was also among them.
Zcash
Transactions in the Zcash network can be both transparent and private. Users can create a “t” address and “z” address to send and receive transactions. The “t” addresses work the same as bitcoin addresses, while “z” addresses are private, and you will only be able to see the balance in the wallet. By using a “z” address, a user doesn’t need to disclose their address, the recipient address, and the sent amount. At the same time, the interaction between these two addresses’ types is fully implemented.
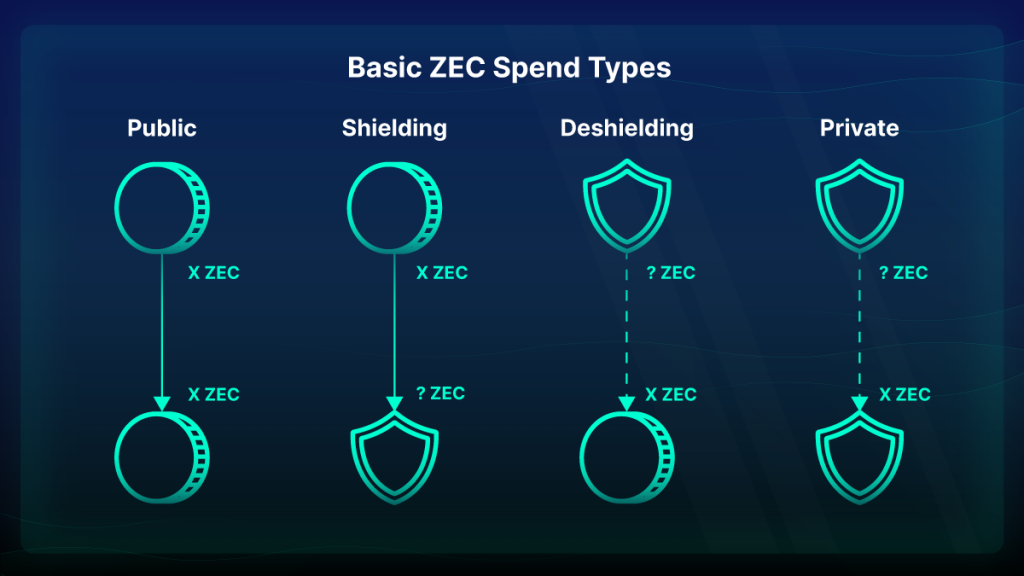
It means that sending crypto from “t” to “z,” or “z” to “z”, or “z” to “t” follows the same procedure. You can learn more about how to use Zcash for private transactions here.
Dash
The Dash cryptocurrency and the identically named blockchain were originally positioned as a privacy network called “Darkcoin,” but the developers abandoned the privacy concept in 2015. Instead, the project’s CEO, Ryan Taylor, reminded users in 2021 that all Dash transactions are entirely transparent since it is a modernized fork of Bitcoin, which is kept running on the public blockchain.
However, Dash allows for relatively anonymous transactions using the CoinJoin mixer.
“The technology that Dash utilizes in our PrivateSend function is CoinJoin, which is a technique for complicating transactions to the point that they’re more difficult for analytics firms to analyze”
said Fernando Gutierrez, CMO for the Dash Core Group
Monero
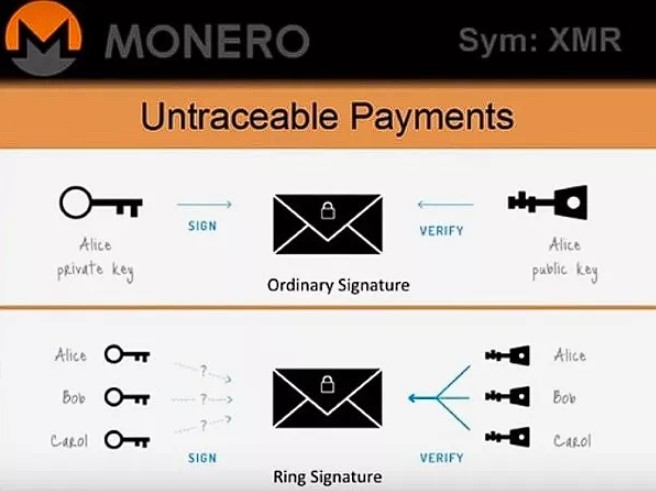
Monero can be called a genuine privacy chain. Unlike Zcash, the Monero network makes it impossible to choose between private and transparent transactions. This protocol works in such a way as to hide all network events and their details. The Monero blockchain is an ideal environment for research and interaction for all fans of total privacy in decentralized networks.
The Monero network uses “stealth addresses”, which are addresses that are dynamically changed for each new transaction. “Ring signatures” are used in Monero when a transaction’s signature has been created based on different keys from several unknown users (with the reverse of the process being impossible). Also, “ringCT” hides the amount of XMR sent in a transaction.
Other Privacy Cryptocurrencies
In addition to Zcash and Monero, the Decred (DCR), Oasis Network (ROSE), and Horizen (ZEN) projects are also included in the top 5 cryptocurrencies by market capitalization.
Decred is mostly a pseudonymous network, where users may use the CoinShuffle++ (CSPP) tool, created on the CoinJoin mixer base. It helps them to mix their coins with other participants and makes it difficult to track their transaction history.
Oasis Network positions itself as the first blockchain to support confidential smart contracts. The runtime of this blockchain is confidential, and ParaTime uses secure enclaves to keep data private while being processed.
Horizen provides developers with tools for creating and developing blockchains or DeFi protocols. Projects such as Dash, Morpheus.Network, IOTA, and others are already collaborating with the Horizen platform.
Interesting fact: Placing 6th in the market cap ranking of privacy blockchains, the Secret network (SCRT) also allows developers to create and execute privacy-preserving smart contracts. This project supports encrypted inputs and outputs and an encrypted state for smart contracts. The Secret network combines Ethereum’s smart contracts, Monero’s privacy solutions, and the Cosmos blockchains as its basis.
Are Privacy Coins Illegal?
Despite the vague position of cryptocurrencies in the legislative field, privacy coins like Monero have attracted additional attention from regulators. For example, Australia and South Korea have vehemently opposed CEXs providing access to privacy coins.
The US Internal Revenue Service has also tried de-anonymizing transactions on privacy networks. In September 2020, the IRS awarded two $625,000 contracts looking for tracing tools for privacy token Monero and Layer 2 protocols. The winners were the blockchain analytics firms Chainalysis and Integra FEC.
The FATF Travel Rule and the AMLD-5 directive set by the European Union, which provide for the implementation of the “know your customer” rule, can also create problems for privacy coin users.
Join our communities and follow us for more news and articles about the blockchain, DeFi, and the Tezos ecosystem!
Telegram | Twitter | Discord | Reddit | Facebook

